Back 24,000 years, a resurgent microorganism(From resurrection to reproduction)
What if a life that has been frozen for tens of thousands of years comes back to life?
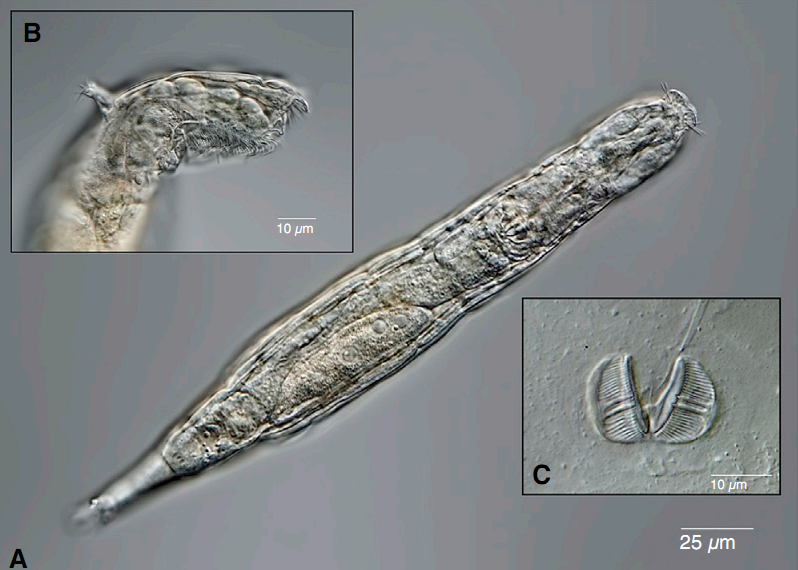
The picture below shows the Bdelloid rotifer,
which had been frozen for 24,000 years, thawed and re-engaged (Fig. 1).

Many people are wondering and challenging
whether it is possible to freeze humans(Fig. 2) like Dooly, a baby dinosaur that came down the glacier(Fig. 3).


Russian researchers have recently confirmed
survival by thawing a multicellular creature called the "Bdelloid rotifer,"
which has been frozen in the Arctic permafrost for 24,000 years.
The findings were recently published in Current biology (Fig. 4).

The Bdelloid rotifer, who survived 24,000 years, was able to reproduce normally.
It has been confirmed to be possible in multicellular organisms with brains, organs, muscles, and reproductive organs (Fig. 5).
Russian scientists have discovered this Bdelloid rotifer
frozen in a specimen dug a hole 3.5 meters deep
in the permafrost of northeastern Siberia (Fig. 6-7).


The researchers used radiocarbon dating in the area
where Bdelloid rotifer was discovered to estimate the time
it lived about 24,000 years ago.
In response, Dr. Stas Malavin told The New York Times,
"We resuscitated an animal that witnessed a living furry mammoth." (Fig. 8)

Bdelloid rotifer is a representative extreme environmental resistance creature
along with water bears (Fig. 9) and Sleeping Chironomid (Fig. 10).


The study of living things that survive in these extreme conditions is meaningful in two contexts.
The first is the freezing preservation of life.
Researchers expect that these examples,
which are conserved in extreme environments for tens of thousands of years,
will enable them to be conserved at the cellular level to the multicellular population level.
The second is space exploration.
The environment that mankind must face in space exploration is extreme.
The study of defensible life forms against this extreme environment
will contribute to the exploration and protection of the human universe.
However, researchers have not been able to explain
the mechanisms by which such creatures can resist extreme conditions.
We're looking forward to further researches.
